Tendons are tough and fibrous cords that attach the bones to the muscles. Healthy tendons are made of parallel and straight fibers of collagen. A painful tendon in the elbow, hip, shoulder, ankle, or knee can be a troublesome condition. For such conditions, most people are familiar with the concept of tendonitis or an inflamed tendon. But very few are aware of the concept of tendinosis. There is a clear line of distinction between the two and their symptoms and treatments are also different.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is an acutely inflamed swollen tendon that does not have any microscopic tendon damage. The condition is characterized by redness, swelling, and warmth of the affected area along with acute pain. Microscopic testing shows the presence of inflammatory cells.
Tendinosis
Tendinosis is the non-inflammatory degeneration of a tendon that includes changes to the composition or structure of a tendon. While the condition can be painful, there is no sign of redness or warmth of the surrounding soft tissues. When examined under the microscope, there will be microscopic signs of tearing of the tendons but no evidence of inflammatory cells.
Some of the key differences between the two are –
Unlike tendonitis, tendinosis may take several months to cure.
The treatment method for tendonitis and tendinosis may vary. Experts highly recommend not treating tendinosis with corticosteroids and NSAIDs as that will inhibit the normal reconstruction of the tendon and weaken the structure.
Tendinosis usually affects people who are involved in high-intensity activities or sports that require frequent tendon movement.
Anatomy
Once you understand the anatomy of tendonitis, you can understand how the tendons become injured and the necessary steps that need to be taken for its treatment. Tendons are the structures that attach the bones to the muscles, but most people misunderstand the attachment part.
Tendons are made up of fascia that contains:
- White and yellow fibers: These are stretchy components of connective tissues present in the tendons. Since tendons hardly stretch, it is the muscles of the tendons that stretch. So, there are not many white and yellow fibers present in tendons.
- Collagen fibers: This is a fibrous material that is incredibly strong and is found in the highest concentration in the skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments. As tendons connect the muscle to the bone, the presence of collagen fibers provides strength to lift the weight of the arms and legs.
- Ground substance: This is the fluid component of all connective tissues that helps the tissues to slide and glide in the body. The presence of a ground substance in tendons is less which keeps the gliding and sliding of the tendons to a minimal.
Effect of this anatomy on tendonitis
Whenever there is any motion of the body, such as swinging a tennis racket, the muscles contract transferring the force through the tendons to the bones resulting in such movement.
When there is a constant contraction of the muscles, there is little chance of the muscle to stretch out again. This exerts a constant pull on the tendons. This repeated contractions of the muscles and inflammation lead to the development of tendonitis injury.
What Causes It?
The most common cause of tendonitis is due to the repetitive and minor impact on the affected area. it may also be a result of a more serious injury. Some of the activities that can lead to such an occurrence are –
- Raking
- Gardening
- Shoveling
- Carpentry
- Painting
- Playing tennis
- Scrubbing
- Throwing and Pitching
- Golfing
Besides these, improper posture at home or work or lack of appropriate conditioning before exercise can increase the risk of tendonitis. The other risk factors include –
- Overuse of the tendons or repeating a task more frequently can increase the possibility of tendonitis problems.
- A joint that is affected by arthritis may also exert increased pressure on the soft tissue structures causing tendonitis.
- Stress on the tendons due to other health conditions such as gout, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disorders, and psoriatic arthritis, or any other abnormal medical reaction.
Tendonitis symptoms
The symptoms of tendonitis also referred to as overuse tendinopathy, include –
- Dull pain or tenderness near a joint, especially around the wrist, shoulder, ankle, or elbow.
- Stiffness, along with the pain that restricts the movement of the joint.
- Thickening or mild swelling of the tendons near the joint.
You need to call the doctor for your tendonitis problem if –
- The pain does not ease up, or it may lead to the development of
- The pain is excruciating, accompanied by marked loss of motion or swelling. That may be a sign of a ruptured tendon that would require immediate medical attention.
Types of Tendonitis
There are different types of tendonitis that affect different parts of the body.
Supraspinatus Tendonitis
In the case of supraspinatus tendonitis, the tendons located around the top of the shoulder joint becomes inflamed, arousing pain with arm movement, especially in the upward direction. Some people may experience pain while lying in the affected shoulder at night. The patient is suffering from rotator cut syndrome if all the other tendons in the same area are affected.
Achilles Tendonitis
This tendon is located between the calf muscles and the heel. The Achilles tendonitis is a sports injury that may be a result of shoes that do not provide adequate support the foot. It is more pronounced among patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis.
De Quervain’s Stenosing Tenosynovitis
The sheath located between the thumb and the wrist gets inflamed. The condition involves thickening of the sheath and swelling in the area, making it painful to move the thumb.
Tennis Elbow or Golfer’s Elbow
This is a symptom of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow, where the person experiences discomfort on the outside of the elbow. The pain may gradually move down towards the wrist. In the case of medial epicondylitis or golfer’s elbow, the pain arises on the inside portion of the elbow. This pain also radiates down towards the wrist with the patient experiencing excruciating pain trying to lift the elbow against a force.
Tendonitis of The Wrist
The problem is commonly seen among workers in the production line and badminton players who repeat the same action with their wrist. This is not an inflammation but a degenerative condition.
Trigger Finger or Thumb
Due to thickening and inflammation of the sheath in the palm of the hand, the finger or thumb stays in a bent position and does not allow the tendons to move smoothly. Sometimes a nodule is formed along the tendon, making the thumb or finger click when straightened out.
Tendonitis treatment
The treatment for tendonitis aims to eliminate pain and reduce inflammation. Some of the commonly followed treatment options include –Resting the Joints
With prolonged rest from any physical activity such as typing or sporting activity, causing the tendonitis problem, the inflammation with go down. Wrapping the affected area with a bandage, brace or splint may keep movement to a minimum. In severe conditions, the affected area may require a plaster.
Applying Heat or Cold
Applying a warm towel or a pack of ice to the affected area can reduce the pain and swelling. Ice can be applied for about 10-15 minutes twice daily. However, do not apply ice on the skin directly, either wrap the ice in a towel or apply an ice pack. You can also take a warm bath or apply a hot towel prior to applying any topical medication.
Pain Relievers
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and ibuprofen can provide relief from tendon pain.
- Getting the affected area massaged can also expedite the healing process.
- Specific stretching exercises, as recommended by a physical therapist, can strengthen the affected muscles and tendons.
- Applying corticosteroid injections around the tendon may alleviate symptoms of tendonitis.
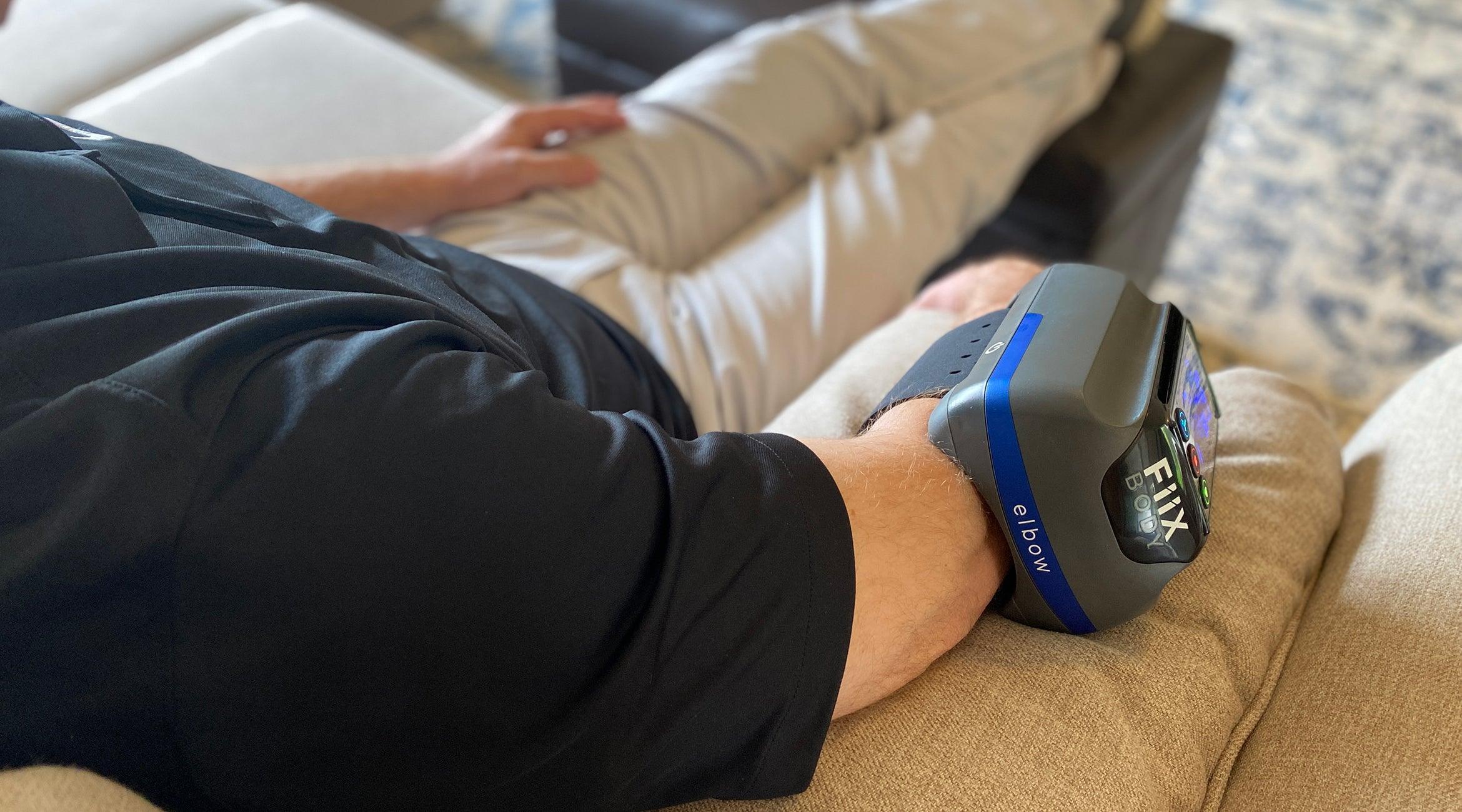
Fiix Elbow program
The at-home tennis elbow or golfer's elbow program automates a proven, clinical procedure called instrument assisted soft tissue mobilization (IASTM). It applies a deep massage to the injured area to break up adhesions and scar tissue to recruit oxygen rich blood to the area to begin the healing process.